SCOPE:
This report presents the
results of an ISO 5011 test of several air filters designed for the GM Duramax
Diesel. The test was independently performed under controlled conditions using
a $285,000 machine at Testand Corp of Rhode Island (manufacturer of the
machine). Arlen Spicer, a GM Duramax Diesel owner/enthusiast organized the
test. Ken an employee of Testand offered to perform the tests at no charge.
(These tests typically cost approx $1700.00 per filter). Ken, also a Diesel enthusiast and owner of a
Ford Power Stroke Diesel, shared Arlen s interest in performing an accurate
unbiased test of different types and brands of diesel engine air filters. The
filters used in the test were purchased retail and donated by Arlen and other
individual Duramax Diesel owners. The detailed reports from the test have been
compiled and are presented in the following pages. The final pages of this
report present the behind the test.
ISO 5011 Test:
The ISO 5011 Standard
(formerly SAE J726) defines a precise filter test using precision measurements
under controlled conditions. Temperature & humidity of the test dust and
air used in the test are strictly monitored and controlled. As Arlen learned in
attempting his own tests, there are many variables that can adversely affect
filter test results. A small
temperature change or a small change in humidity can cause the mass of a paper
filter to change by several grams. To obtain an accurate measure of filter
efficiency, it s critical to know the EXACT amount of test dust being fed into
the filter during the test. By following the ISO 5011 standard, a filter tested
in Germany can be compared directly compared to another filter tested 5 years
later in Rhode Island. The ISO 5011 filter test data for each filter is
contained in two test reports; Capacity-Efficiency and Flow Restriction.
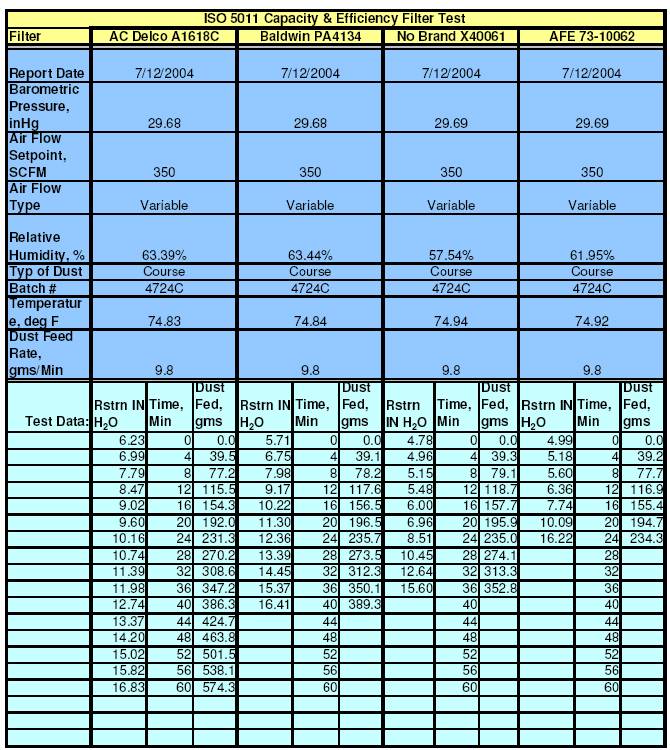
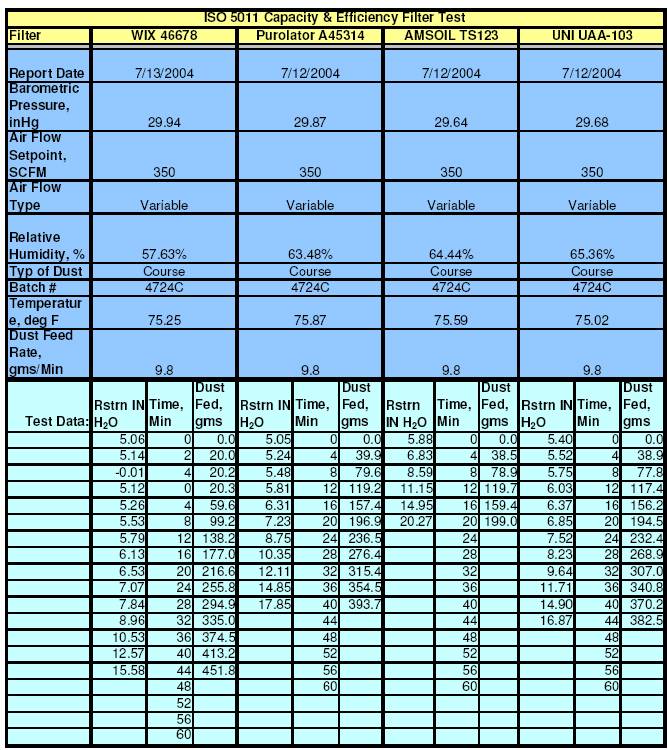
Capacity and Efficiency:
The Capacity and Efficiency
test report presents the test results of feeding an initially clean filter with
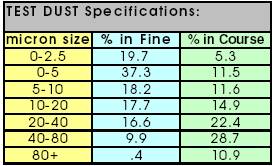
PTI Course Test Dust (dirt) at a constant rate and airflow. The course
test dust has a specific distribution of particle sizes ranging from less than
2.5 microns to greater than 80 microns (see table below). Every filter is
initially tested at 350 CFM and the Initial Restriction or differential
pressure across the filter is recorded in IN-H20 (Inches of Water).
The filter is then tested by feeding test dust at a nominal rate of 9.8 grams
per minute with a constant airflow of 350 CFM. The test is continued until the
flow restriction exceeds the Initial Restriction + 10 IN-H20.
At this point the test is terminated and the amount dust passed through the
filter - Accumulative Gain - is measured. Dirt passing through the
filter is captured in the Test Station s Post Filter. The exact amount
of dirt passed is determined by measuring the before and after weight of the Post
Filter. Similarly, the amount of dirt retained by the Filter under test - Accumulative
Capacity is measured by taking the difference between the before and
after weights of the Filter. From these results the overall % Efficiency
of the filter is calculated. This test
also indicates how long a Filter will last before replacement is required (or
cleaning for reusable filters).
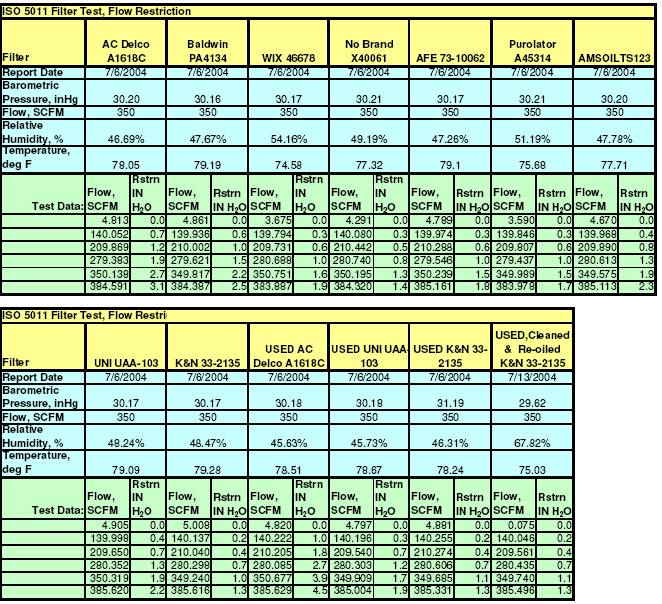
Flow Restriction:
This report presents flow
restriction of a clean filter resulting from an increasing airflow. The
differential pressure restriction across the filter is reported in inches of
water (IN H2O) versus Air Flow in cubic feet per minute CFM.
Data from these reports has
been compiled and presented in the following bar graphs, Plots and data tables.
Filter Efficiency:

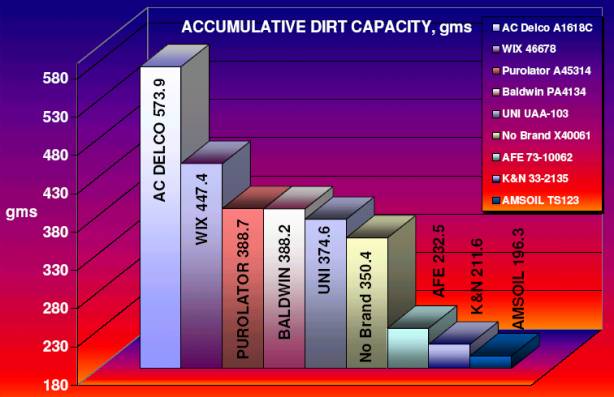
Accumulative Capacity:
Accumulative Capacity is a
measure of dirt holding/loading capacity before reaching the maximum restriction
limit - Initial Restriction + 10 IN-H20.
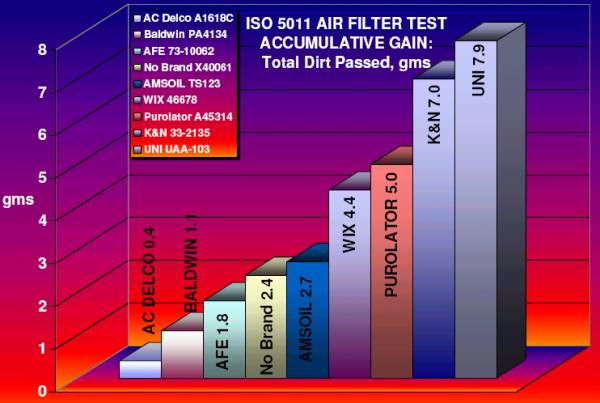
Accumulative Gain:
"Accumulative
Gain" is the total amount of dirt that passed through the filter during
the test.
(Note: The Purolator was reported to have a seal malfunction during the test and passed more dirt than it would have with a good seal.)
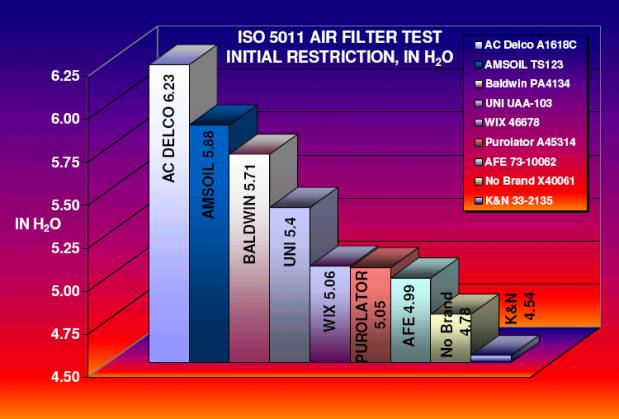
Initial Restriction:
Initial Restriction is the
Filter under test s resistance to flow at 350 CFM.
Dirt Passed Versus Total Test Time
This graph shows each the
duration of each filter s test versus dirt passed (Accumulative Gain).
(Note:
The Purolator was reported to have a seal malfunction during the test and
passed more dirt than it would have with a good seal.)
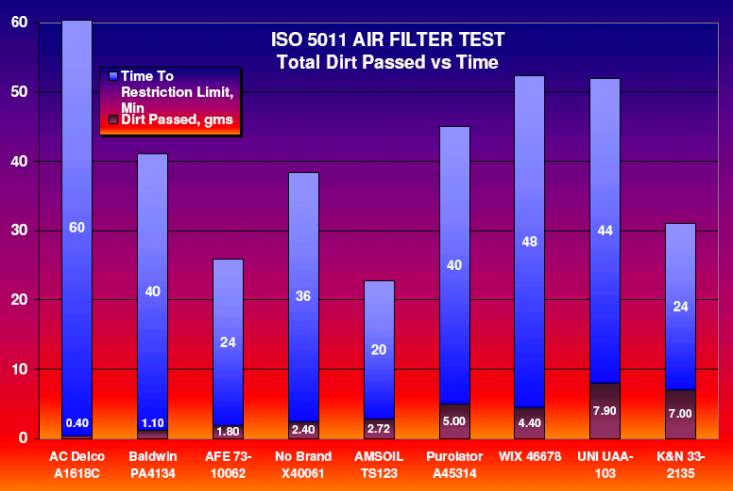
In the chart above it s
important to note the different test durations for each filter. The AC Delco
filter test ran for 60 minutes before exceeding the restriction limit while the
AMSOIL and K&N tests each ran for 20 and 24 minutes respectively before
reaching max restriction. In 60 minutes the AC Filter accumulated 574gms of
dirt and passed only 0.4gms. After only 24 minutes the K&N had accumulated
221gms of dirt but passed 7.0gms. Compared to the AC, the K&N plugged up nearly 3 times faster, passed
18 times more dirt and captured 37% less dirt. See the data tables for a
complete summary of these comparisons.
Dust Loading:
The dust loading curves show
graphically how each filter responded to a constant 9.8 gms/min dust flow
before reaching the maximum restriction limit.
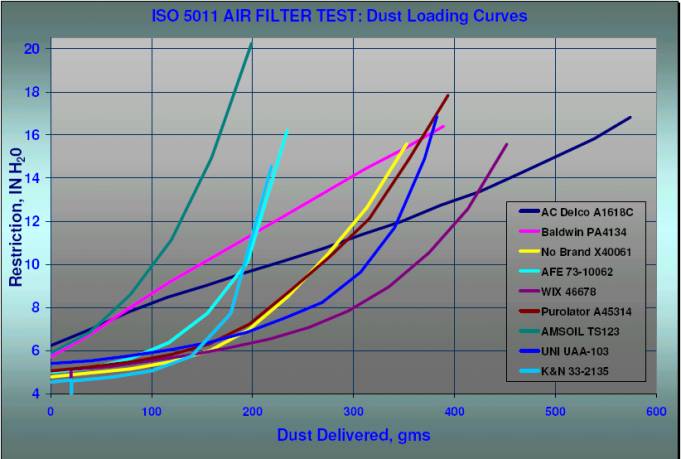
It s interesting to note the
shape of these Dust Loading Curves. The AC and Baldwin filters each had near
linear responses until reaching maximum restriction. Restriction for these
filters increased at a constant rate versus the 9.8 gms/min dust feed rate. The
other filters, most notably the oiled reusable types, had an exponential
loading response before reaching maximum restriction. These filters had a lower
initial restriction, but they became exponentially more restrictive under a
constant flow of dirt. Also notice the length of the curves as it shows the
relative test time for each filter (time to max restriction).
Restriction to Flow:
The Restriction to Flow
curves graphically show how each clean filter responded to a steadily
increasing flow of air up to 350 CFM.
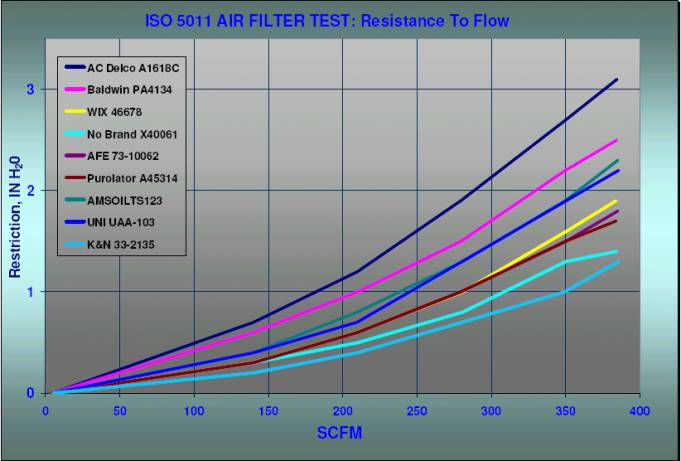
The Flow Restriction
response curves for each filter have the same basic shape. However, note how
the AC Filter, which passed the smallest amount of dirt and had the highest
dirt capacity and efficiency, also had the highest relative restriction to
flow. The less efficient filters correspondingly had less restriction to flow.
This illustrates the apparent trade-offs between optimizing a filter for dirt
capturing ability and maximum airflow.
Test Data Tables:
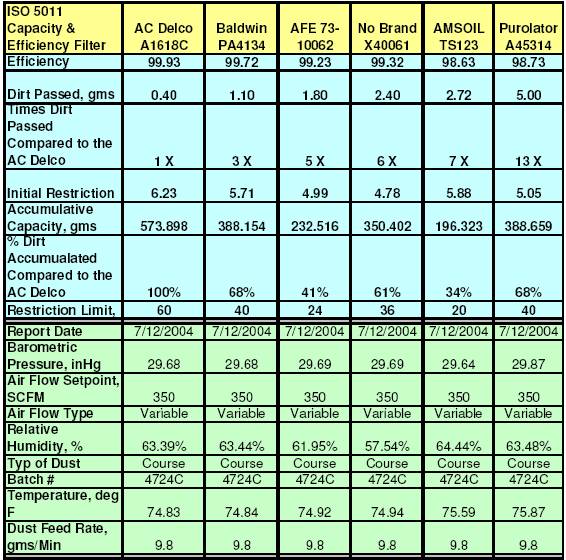
Test Data Tables:
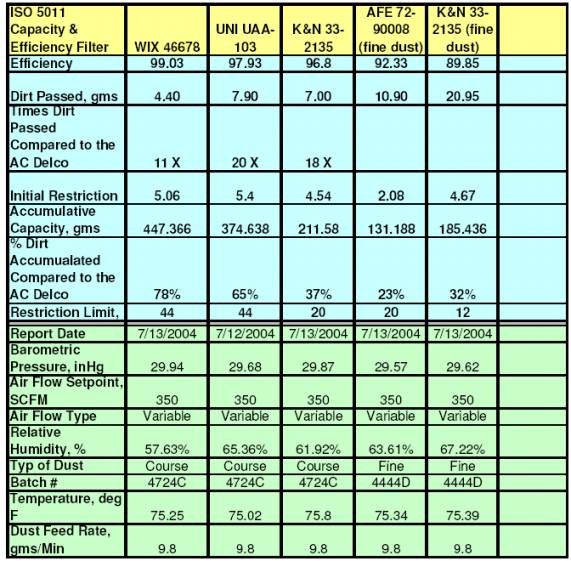
Test Data Tables:
Test Data Tables:
Test Data Tables:
Test Data Tables:
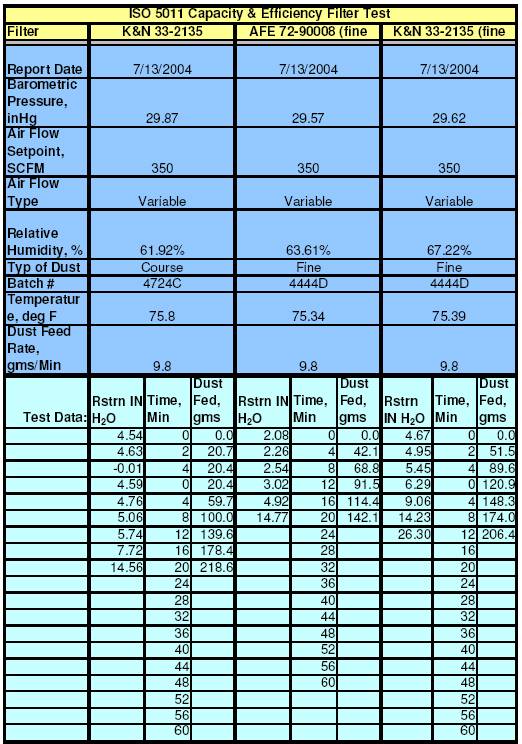
To be consistent with common industry practice all filters
were tested using PTI Course Test Dust. Course dust is more commonly used since
it will produce higher % efficiency numbers.
The Story behind the
test:
First of all, many thanks to
Arlen Spicer and Ken at Testand for organizing and facilitating the test. Arlen
is a professional Firefighter who also operates a small tree service on the
side. The tree service is the reason he owns a diesel truck. This study was the
result of nearly a year of work by Arlen to get accurate independent data on
air filters for the GM Duramax Diesel. Arlen originally set out to build his
own Filter Test Stand so that he could perform accurate, repeatable and
independent measurements on the various filters available for the Duramax.
Arlen questioned the claims made by aftermarket filter manufacturers that their
filters were superior to the conventional OEM style paper filters. After
spending many months, hours and a considerable amount of his own money, he
learned first hand how difficult it was to perform an accurate air filter test.
He found it was difficult to maintain all the necessary controls to insure an
accurate measurement. It was at this juncture that Arlen received a call from
Ken at Testand offering to perform the ISO 5011 test free of charge. Ken found
Arlen s idea for an independent comparison study very interesting and offered
to do the ISO 5011 testing using one of Testand s industrial Filter Test
Machines. Arlen posted the news on the Internet and immediately offers from
other Duramax owners to purchase and send filters for the test started rolling
in. Some purchased and donated filters and others made contributions to cover
the expenses and the cost of shipping the filters to Teststand. It was truly a
team effort. The end result is the top quality data presented in this
report. The following is a quote from
Arlen.
(Arlen) SPICER wrote,
Now that I am not doing
the tests and my objectivity is not necessary, let me explain my motivation.
The reason I started this crusade was that I was seeing people spend a lot of
money on aftermarket filters based on the word of a salesperson or based on the
misleading, incomplete or outright deceiving information printed on boxes and
in sales literature. Gentlemen and Ladies, Marketing and the lure of profit is
VERY POWERFUL! It is amazing how many people believe that better airflow = more
power! Unless you have modifications out the wazoo, a more porous filter will
just dirty your oil! Some will say " I have used aftermarket brand X for
XXX # years with no problems. The PROBLEM is you spent a chunk of ching on a
product that not only DID NOT increase your horsepower, but also let in a lot
of dirt while doing it! Now how much is a lot? ANY MORE THAN NECESSARY is TOO
MUCH!
Others are persuaded by the claims of aftermarket manufacturers that their
filters filter dirt "better than any other filter on the market."
Sounds very enticing. To small timers like you and me, spending $1500 to test a
filter sounds like a lot. But if you were a filter manufacturer and you
believed your filter could filter dirt better than any other media on the
market, wouldn't you want to prove it? Guess what. Test your filter vs. the OE
paper. It will cost you $3000 and for that price you will have the data that
you can use in your advertisements. Your investment will be returned a thousand
fold! EASIER than shooting fish in a barrel! So why don't these manufacturers
do this? Hmmm? Probably not because they would feel guilty about taking more
market share.
Now I am not saying that
ALL aftermarket filters are useless. A paper filter does not do well if
directly wetted or muddy. It may collapse. This is why many off-road filters
are foam. It is a compromise between filtering efficiency and protection from a
collapsed filter. Now how many of our trucks collapse their filters from mud
and water? However, if a filter is using "better airflow" as their
marketing tool, remember this....Does it flow better? At very high airflow
volumes, probably. BUT, Our trucks CAN'T flow that much air unless
super-modified, so what is the point? The stock filter will flow MORE THAN
ENOUGH AIR to give you ALL THE HORSEPOWER the engine has to give. And this
remains true until the filter is dirty enough to trip the air filter life
indicator. At that point performance will decline somewhat. Replace the filter
and get on with it.
Hopefully the results of this test will do 2 things. Shed some light on the
misleading marketing claims of some aftermarket manufacturers and/or give us
new insight on products already on the market that are superior to our OE
filter. I stand for truth and will eat my words publicly if my statements prove
wrong. I appreciate all of the help and support that you members have offered
in this project. It would simply be impossible without your help. A huge thanks
to Ken at Testand for his willingness to take on this project. I would be
spinning my wheels from here to eternity without his help SPICER
Our thanks to Arlen and Ken
for making the test happen and providing the valuable test results for the
benefit of all.
Sept 2004